#1. How to Take Integer Input From User In Java Using Scanner Class??
Very simple basic java program through which we can get inputs from the user in the form of integer and then at the output, we will get those inputs and also sum of those inputs as well using Scanner Class.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class UserInput{
public static void main (String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); // to get inputs from users
System.out.println("Enter 1st Number");
int number1 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter 2nd Number");
int number2 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Your Entered Number is");
System.out.println(number1+ " and " +number2);
int sum = number1 + number2;
System.out.println("The sum is: " +sum);
}
}When you run the above program, the Output looks like:
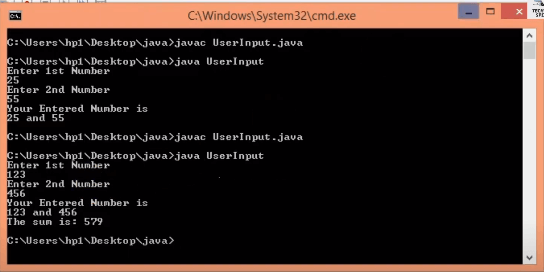
Watch the video below for complete explanation of the above program step by step:
MORE CORE JAVA PROGRAMS
- What is Interface In Java and What are its Uses?
- Java Scanner Class(User Input) with Example
- This, Super and Final keywords in Java with Examples
- What is Encapsulation in java | Java Encapsultion | Getters and Setters
- Abstraction | Java Abstraction OOPs | Abstract Class and Method
- What is Polymorphism in Java | Java Polymorphism
- What is Inheritance in Java? Java Inheritance types
- What is Constructors in Java | Java Constructor
- Loops in Java | Java Tutorial | For | While | For-Each | Do-While
- What is hashmap in java | mapping in java | hashmap java



